Juggling hundreds of tasks and chasing your tail in the business world has become a common sight. Disorganization, miscommunication, and inefficiency often take place without clear step-by-step processes.
An operations manual can help you avoid this struggle! It is a comprehensive document that outlines a business or organization’s processes, procedures, and policies.
In this blog, we will discuss how to create an operations manual, what are its benefits, and explore some examples.
What Is an Operations Manual?
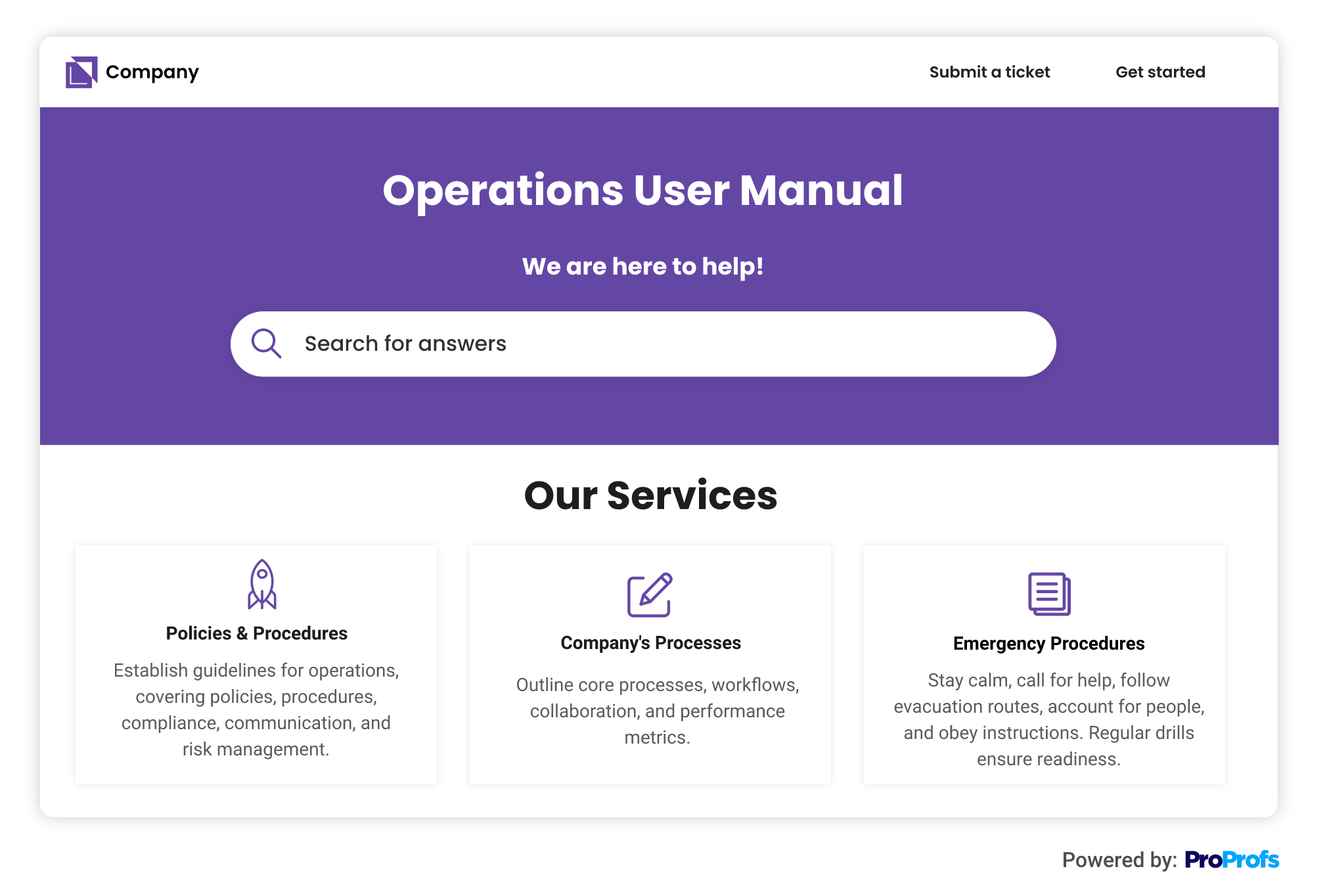
An operations manual is an extensive document that outlines a business or organization’s processes, procedures, and policies. It serves as a reference guide, providing detailed instructions, guidelines, and best practices for every aspect of the business operations.
The manual is essential in ensuring operational efficiency by providing a standardized framework for employees. It is a go-to resource for routine tasks and unexpected challenges, fostering consistency, reducing errors, and enhancing overall productivity.
For example, in software companies, the operations manuals would dictate coding standards, version control processes, release management, bug tracking procedures, security protocols, and deployment processes.
What Should an Operations Manual Include?
An operations manual captures valuable institutional knowledge and helps to ensure that critical tasks can be carried out consistently, regardless of staff changes or turnover.
So, it becomes vital to have all the essential information in the manual. Let’s discuss what those are.
Introduction
Start with an overview introducing your company, its mission, vision, and core values. Provide a brief history and share your business goals and objectives. This section sets the context for the rest of the manual.
Organizational Structure and Roles
Describe the hierarchy of your company, outlining each role and its responsibilities.
Add an organizational chart and define reporting relationships. This helps employees understand the structure and their place within the organization.
Job Descriptions
Provide detailed descriptions for each role, outlining responsibilities, tasks, and required qualifications. Clearly define expectations to ensure clarity among employees and avoid confusion in their duties.
Policies and Procedures
Document your company’s policies and procedures that employees need to follow.
This could include guidelines on topics like code of conduct, attendance, leave, performance management, workplace safety, data security, and IT usage. Specify essential rules and guidelines about specific departments or functions.
Business Processes
Elaborate on the step-by-step procedures for critical business processes. Mention how tasks are performed, including any specific tools, software, or equipment used.
Use diagrams, checklists, or flowcharts to make it easier for employees to understand and follow these processes accurately.
Training and Onboarding
Include information on training programs and onboarding processes for new hires. Outline the training materials, resources, and processes required to ensure successful integration into the company.
Customer Service Standards
Define your company’s customer service standards and expectations. Outline the process for handling customer inquiries, complaints, and feedback.
Provide guidelines on maintaining a positive customer experience and handling difficult situations.
Safety Protocols
Document safety procedures and guidelines to ensure a safe working environment.
Add information on emergency evacuation procedures, fire safety protocols, first aid procedures, and other relevant safety measures.
Communication Channels
Specify the different channels of communication within the organization.
Include information on email protocols, meeting procedures, internal communication platforms, and how information is shared with employees.
Tools and Resources
Provide information on the software, tools, and resources employees need to perform their tasks efficiently. Include instructions, FAQs, or troubleshooting guides for commonly used tools.
Contacts and References
Include a directory of important employee contact information like HR, IT support, suppliers, or emergency services. Also, provide references and resources that employees can refer to for further information or support.
Continuous Improvement
Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by including a section to collect employee feedback and suggestions. This can help identify areas for improvement and promote innovation within the organization.
Benefits of Using Operations Manuals
Investing time and resources in creating an operations manual brings multiple benefits, like a centralized resource, enhanced accountability, and more. Let’s discuss these benefits.
Enables Resource Centralization
An operations manual serves as a central repository of knowledge for your business.
It combines all the essential information, policies, procedures, and guidelines in one place, making it easily accessible to employees.
Having a centralized resource eliminates the need for employees to search for information across different sources, saving time and effort.
Builds Accountability
An operations manual outlines roles, responsibilities, and expectations for each position within the company.
By clearly defining these areas, it sets up accountability among employees.
When everyone knows their responsibilities and understands how their work contributes to the organization’s overall goals, it promotes a sense of ownership and accountability.
Establishes a Lasting Knowledge Base
As a business grows and scales, essential knowledge, and information could get lost if not properly documented.
An operations manual serves as a lasting knowledge base, capturing the collective information and experience of the organization.
It ensures that vital information, processes, and best practices are preserved and passed on to new employees or team members, preventing knowledge gaps and promoting continuity.
Facilitates More Efficient Processes
The operations manual documents standard operating procedures and workflows for various business processes.
Defining clear and standardized processes enables employees to perform tasks consistently and efficiently.
This consistency helps streamline operations, minimize errors, and improve productivity.
Optimizes the New Hire Training
A well-documented operations manual significantly speeds up new employees’ onboarding and training process.
Instead of relying purely on verbal instructions or ad-hoc training, new employees can refer to the manual to understand their roles, responsibilities, and how to perform their tasks.
This reduces the time and effort required for individualized training and ensures that all employees receive consistent and extensive training.
How to Create an Operations Manual



Whether it’s outlining step-by-step processes, defining roles and responsibilities, or documenting troubleshooting procedures, an operations manual enables a single source of truth for all operational activities within a business.
Let’s discuss the steps to create a comprehensive operations manual:
Outline Your Manual: Create a Clear Structure
The first step is to create a structured and organized outline for the manual. Categorize the manual into clear sections and sub-sections that align with the different areas of your business operations.
For example, you can organize your manual into sections like administrative procedures, operational processes, HR policies, customer service, safety protocols, and emergency procedures. This outline will serve as a guide to ensure that you cover all necessary content.
Key Company Information: Provide Context and Insight
Start the manual by providing an introduction to your business, including your company’s mission, vision, and core values.
Provide information about your business’s history, goals, and objectives. You can also include an overview of your company’s products and services.
Map Your Organizational Hierarchy: Understanding Roles & Reporting
Include a clear organizational chart that explains the hierarchy of roles and reporting relationships within your company. This will help employees understand the organization’s structure and how different roles fit together.
Ensure that each role is clearly defined and that employees understand their place within the company hierarchy.
Job Descriptions & Contact Details: Specify Responsibilities & Connections
Define the responsibilities, expectations, and qualifications for each role within your organization. Detail the job descriptions that outline critical tasks, authorities, and required qualifications.
Add contact details for each employee, including their name, position, email, and phone number. This will allow employees to reach out to their colleagues when necessary.
Document Business Processes: Capture Efficient Workflow
Document step-by-step procedures for all core business processes, from sales and marketing to production and customer support.
Include detailed instructions, diagrams, checklists, and other relevant information to ensure consistency and accuracy in executing these processes. This will help reduce errors and increase efficiency across the organization.
Company Policies: Establish Guidelines & Standards
Outline the policies and guidelines employees should adhere to. Address areas like the code of conduct, employee benefits, time-off policies, IT usage, data security, and other policies specific to your business.
Communicate your expectations to promote a harmonious and compliant work environment. Ensure that employees know your policies and understand the implications of non-compliance.
Emergency Procedures: Ensure Safety & Preparedness
Elaborate on emergency instructions like fire drills, evacuation plans, and safety protocols. Ensure employees are well-informed about what to do in emergencies to ensure their safety and minimize potential risks.
Regularly review and update your emergency procedures to ensure they are current and relevant.
Provide Additional Contact Information: Connecting With Essential Partners
Besides employee contact details, include the contact information for other key stakeholders like suppliers, clients, contractors, or emergency services.
This ensures that employees have quick and easy access to essential contacts they may need to contact during work. Also, provide information about relevant support services like IT support, legal advice, or HR services.
Make Your Manual Accessible: Publish for Easy Reference
Once your operations manual is complete, ensure it is easily accessible to all employees. It’s safer to publish it on a shared drive, an intranet platform, or a dedicated company portal.
Communicate any changes or revisions to the manual to ensure its effectiveness and relevance. Encourage regular reviews of the manual by all employees to ensure its continued effectiveness.
Read More: How to Create an Operations Manual for Your Business
How to Update and Distribute Your Operations Manual
It’s essential to ensure your operations manual is updated and shared regularly as your business evolves and changes.
Let’s discuss the steps to update and distribute your operations manual:
Identify Necessary Updates
Analyze your manual regularly to identify necessary updates. Company policies, processes, or personnel changes should be reflected in the manual to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Highlight the Updates
Once you are sure about the necessary updates, highlight them in the manual or create a summary. This makes it easier for employees to identify what information has been added or updated.
Review the Manual with Team Leaders
Before finalizing the changes, it’s essential to review them with team leaders or department heads to ensure the updates are accurate and reflect the current processes and policies.
Finalize the Updates
Once you’ve reviewed the updates with team leaders and gathered their input, make the necessary changes to the manual. Ensure that the changes are clear and accurate.
Get Approval
Once the updated manual is finalized, get approval from upper management or a relevant authority before distributing it to employees.
This ensures everyone knows the updates and that the changes align with the company’s objectives and vision.
Distribute the Manual to Key Stakeholders
Share the updated manual with all employees, ensuring they know the updates and understand their significance. If required, you may share the manual with advisors, investors, etc.
Usually, the manual is shared digitally via the company’s intranet, shared drives, or other relevant platforms. Some companies may distribute a hard copy of the manual as well.
Communicate the Updates
Communicating any significant updates to the manual is essential to ensure employees know the changes and understand their implications.
Consider organizing a meeting or training session to review the changes and answer any employee questions.
Gather Feedback
Encourage feedback from employees on the updated manual. This feedback can be used to identify areas that require further clarification or revisions.
Consider creating a formal feedback mechanism or discussion forum to obtain employees’ views.
Update the Manual Regularly
Regularly review and update the operations manual to ensure it remains accurate and up-to-date with any policies, processes, or personnel changes.
Set a regular schedule to review and update the manual, perhaps annually or whenever significant changes occur.
Create Comprehensive Operations Manuals With Ease!
Operations manual is a valuable resource for training new employees, enabling faster onboarding, and ensuring they understand and follow established processes. Creating the right manual with operations manual software helps streamline procedures and improve task consistency.
ProProfs Knowledge Base helps create operations manuals with the help of pre-designed Knowledge Base templates. You can choose one of the templates or start building your article from scratch. You can import existing files like Word documents or PDFs and edit them within the software. Multiple users can contribute, review, and edit the documents, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Get started with creating insightful and extensive technical documents like operations manuals like a pro! Start now by exploring the tool here!
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!