Technical documentation serves as the backbone of user support and product understanding in the technology sector. It guides users through the complexities of products and services and provides a reference point for developers and stakeholders.
GitHub’s survey reveals that incomplete or outdated documentation is a pervasive problem, observed by 93% of respondents, yet 60% of contributors say they rarely or never contribute to documentation.In this blog, we will discuss the purpose of technical documentation, its types, and its benefits. We will also explore the best practices for creating it, some examples, and explore software for the same.
| Related blog: How to Create Online Documentation? |
What Is Technical Documentation?
Technical documentation is the process of creating documents that explains the use, functionality, creation, or architecture of a product or service.
It’s normally targeted toward users, system administrators, and support staff, but it can also target developers, project managers, or anyone else involved in developing, maintaining, or using an application or system.
It is crucial to ensure that hardware or software products can be used as intended, helping to reduce support costs, improve user experience, and ensure compliance with industry standards or regulations.
A common example of technical documentation is the API documentation provided by software services like GitHub or Google Maps. These documents detail how developers can utilize the API to integrate the service’s functionality into their own applications.
Read More: How to Write Code Documentation
What Is the Purpose of Technical Documentation?
Technical documentation serves several vital purposes, providing a comprehensive guide for various stakeholders in developing, using, and maintaining technology products and systems.
Here are some critical purposes of technical documentation:
User Guidance
Technical documentation provides users with instructions on using a product or system effectively. This can be done using user manuals, quick-start guides, and online help systems.
The objective is to ensure that users can achieve their goals with the product without direct assistance from support staff.
Read More: Best Documentation Tools & Software
Technical Support & Troubleshooting
Technical documentation provides detailed information on troubleshooting common problems, technical specifications, and FAQs.
This helps reduce the volume of support requests and enables users to solve problems independently.
Read More: How to Create Software Documentation
Product Development & Maintenance
For developers and engineers, technical documentation is vital during a product’s development and maintenance phases. It could include API documentation, code comments, system architecture designs, and development guidelines.
These documents help understand the system’s design and implementation, ensuring consistency in future development and easing maintenance tasks.
Training & Onboarding
Technical documentation serves as a training documentation resource for new employees, helping them to understand the product or system quickly.
It can significantly reduce the time and resources needed for employee training by providing an accessible knowledge base.
Compliance & Safety
In regulated industries, documenting technical processes and system specifications is required for compliance with legal and safety standards.
This documentation helps in demonstrating that products meet the required standards and guidelines.
Quality Assurance
Technical documentation is crucial in quality assurance processes, detailing testing procedures, standards to be met, and the criteria for product acceptance.
This ensures that products are developed to meet quality benchmarks consistently.
Read More: How to Create Developer Documentation
Knowledge Preservation
It acts as a knowledge repository, ensuring that critical information is preserved and accessible.
This is especially important in managing staff turnover, as it allows new team members to come up to speed on complex projects quickly.
Communication Tool
Technical documentation facilitates clear communication among various stakeholders, including developers, testers, project managers, and end-users.
Providing a shared reference point helps in aligning understanding and expectations.
Marketing & Sales
Although not its primary role, technical documentation can support marketing and sales by providing detailed product information highlighting features, capabilities, and benefits.
Well-crafted documentation can help potential customers understand a product’s value proposition.
What Are the Types of Technical Documentation?
Technical documentation can be broadly categorized into several types, each serving different purposes and aimed at different audiences.
Let’s discuss the different types of technical documentation and their specifics:
Product Manuals
These comprehensive guides provide all the necessary information about a product, including its features, usage instructions, safety information, and troubleshooting tips.
Product manuals are created to help users fully understand and correctly utilize a product.
Read More: How to Create Product Documentation – Types, Benefits
Repair Manuals
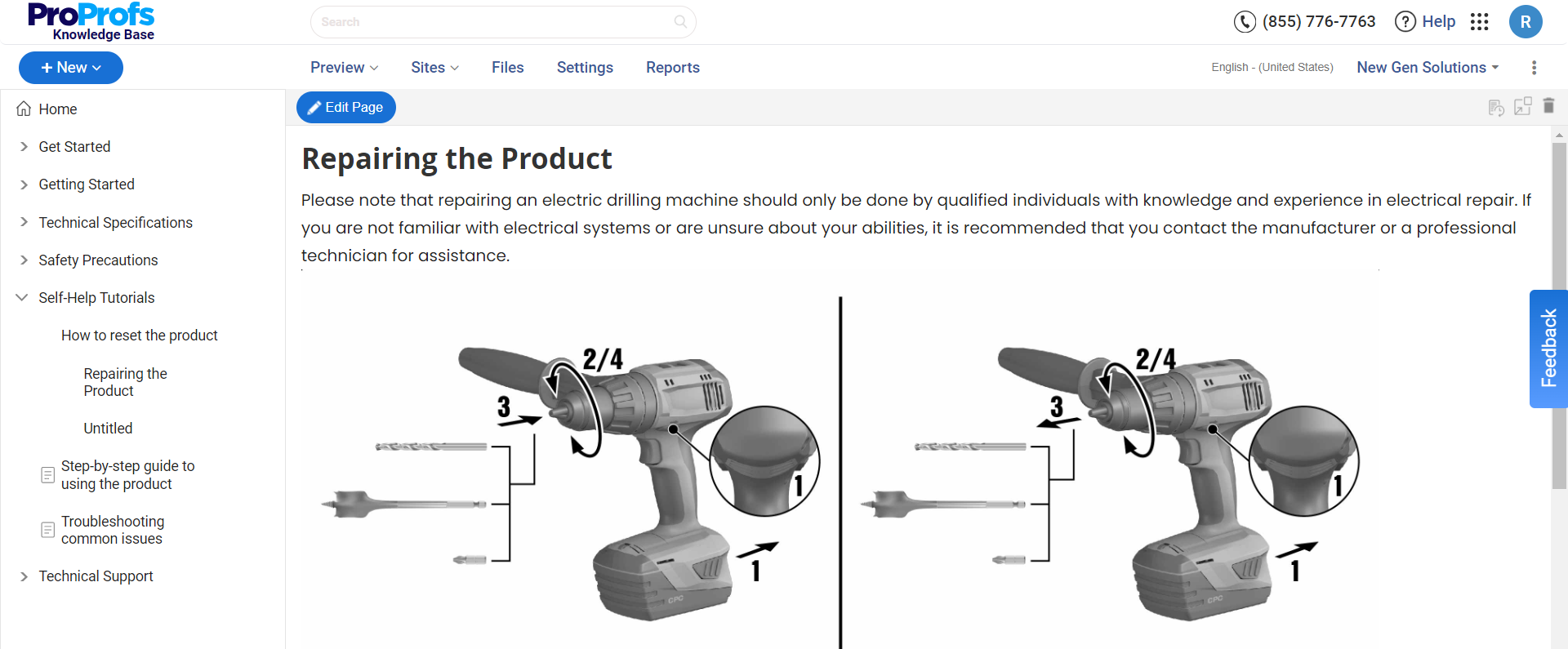
These manuals are aimed at technicians or users with technical knowledge; repair manuals contain detailed information on how to diagnose and fix problems with a product.
They include schematics, parts lists, and repair instructions to facilitate maintenance and repairs.
User Guides
These guides are similar to product manuals; user guides offer instructions on using a product or system but are often more concise.
They focus on common tasks, providing step-by-step guidance to help users achieve specific goals or complete specific operations.
Read More: Best Software Documentation Tools in 2024
API Documentation
This documentation is essential for developers; API documentation describes how to effectively use and integrate with an application programming interface (API).
It includes details on the available functions, classes, return types, arguments, and more, along with examples of how to make requests and handle responses.
Read More: Best API Documentation Tools
SDK Documentation
Software Development Kit (SDK) documentation provides developers with all the necessary information to use an SDK, including installation instructions, feature descriptions, code samples, and guidelines for building applications using the SDK.
Project Plans
These documents outline a project’s objectives, scope, timeline, resources, stakeholders, and methodology.
Project documentation plans are crucial for guiding the team through the project lifecycle, ensuring everyone is aligned and aware of their roles and responsibilities.
Business Standards
Documentation of business standards consists of the policies, procedures, and benchmarks that a company adheres to.
These documents ensure consistency in practices and compliance with industry regulations, quality standards, and ethical norms.
Test Schedules
Test schedules outline the planning for testing phases of a product or system, including what will be tested, how it will be tested, the resources required, and the timeline.
These help ensure thorough testing and quality assurance.
Market Requirements Documentation
This type of documentation covers the needs and requirements of the market a product or service intends to serve.
It includes analyses of target demographics, competitive landscapes, and product requirements based on market research.
Read More: 12 Best User Documentation Examples of Help Guides
White Papers
White papers are authoritative reports or guides that inform readers about complex issues, present the issuing body’s philosophy, and provide comprehensive solutions.
They are used to educate readers and help people make decisions, often in the context of marketing or policy-making.
Case Studies


These documents detail real-world examples of how a company or product has successfully addressed a particular problem or met a specific need of a client or customer.
Case studies are used as a marketing tool to demonstrate the value and effectiveness of a solution.
RFPs & Proposals
Requests for Proposals (RFPs) are documents organizations issue to solicit proposals from vendors or service providers.
Proposals are responses to RFPs detailing how a vendor can meet the project’s needs, including methodologies, timelines, and costs.
What Are the Benefits of Creating Technical Documentation?
Creating technical documentation offers a wide range of benefits that impact various aspects of a business, product lifecycle, and user experience.
Here are some key benefits:
Improved User Understanding & Satisfaction
Extensive technical documentation, such as user guides and product manuals, enables users to understand how to use a product or service effectively.
This results in increased satisfaction and loyalty, as users are less likely to encounter issues and more likely to utilize the product to its full potential.
Enhanced Customer Support
With comprehensive troubleshooting guides and FAQs, many common user issues can be resolved without direct customer support.
This improves the user experience by providing instant help and reduces the workload on support teams, allowing them to focus on more complex queries.
Higher Product Quality & Safety
Technical documentation is crucial in the development and testing phases, detailing specifications, standards, and quality benchmarks that products must meet.
This ensures that the product is developed with a clear understanding of requirements, leading to higher quality and safer products.
Streamlined Development & Maintenance
For developers and technical teams, documentation like API guides, SDK documentation, and system architecture descriptions are indispensable tools.
They provide a clear reference, helping to maintain consistency, facilitate knowledge sharing, and speed up the development and maintenance processes.
Easy Knowledge Preservation
Technical documentation serves as a repository for organizational knowledge. It ensures that critical information is not lost due to staff turnover or the passage of time, making it easier for new team members to get up to speed and reducing the risk of knowledge gaps.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Protection
In highly regulated industries, maintaining detailed records of product specifications, safety guidelines, and compliance with standards is required by law.
Technical documentation helps meet these legal requirements and can provide protection in legal disputes by demonstrating due diligence and adherence to regulations.
Market Penetration & Sales Support
Well-crafted, comprehensive technical documentation can also serve as a sales enablement tool.
Documentation like detailed product specifications, white papers, and case studies help potential customers understand the value proposition of a product or service, aiding in decision-making processes and supporting marketing and sales efforts.
Training & Onboarding Enablement
For new employees or external partners, technical documentation like project plans, business standards, and operation manuals can significantly reduce the learning curve, facilitating quicker onboarding and more effective training processes.
Support for Globalization Efforts
Technical documentation can be localized to accommodate multiple languages and cultural nuances for products and services offered in multiple countries.
This supports globalization efforts by ensuring that users worldwide can effectively use and understand the product.
Feedback Loop & Continuous Improvement
Technical documentation enables a basis for feedback from users and technical staff, which can be used to identify areas for improvement. This feedback loop is essential for continuous product development and enhancement.
Best Practices for Writing Technical Documentation
Writing insightful technical documentation helps users, developers, and stakeholders understand and utilize technology products and systems efficiently. Here are some best practices for writing technical documentation:
Preliminary Research
Start by defining the purpose of your documentation. What problem does it solve? Create an outline or mind map to organize your content.
Understand who your readers are. Are they developers, system administrators, or end-users? Tailor your content accordingly. Write user stories to capture different scenarios as it helps you address specific use cases.
Know Your Audience
Create online documentation with user personas to represent different types of readers. Understand their goals, knowledge level, and pain points.
Map out how users will navigate through your documentation. Consider their entry points and the paths they might take.
Use a consistent tone — formal or friendly, based on your audience. Avoid jargon unless it’s industry-standard.
Navigational Structure & Design
A well-organized TOC is essential. You can organize it by grouping related topics under clear headings. Use hierarchical headings (H1, H2, etc.) to create a logical flow. H1 represents the main topic, followed by subtopics.
Link related sections within your documentation. For example, link from a concept explanation to a detailed procedure.
Template Creation
Technical documentation templates ensure uniformity – create templates for different document types (e.g., installation guides, API references). You can use dedicated technical documentation software with pre-approved knowledge base templates.
Create reusable snippets (e.g., code examples, troubleshooting steps) to insert across documents. If your documentation is version-specific, clearly indicate which version it applies to.
Reader-Friendly Content by Using Multimedia
Break down information into smaller chunks using short paragraphs, bullet points, and numbered lists. Include relevant images, diagrams, screenshots, and videos. Visuals enhance understanding and break up the text.
Incorporate real-world examples and use cases. Show how to apply concepts in practice. Format code consistently. Use syntax highlighting and annotating essential parts. Use callout boxes (e.g., tips, warnings, notes) to highlight critical information.
Choose the Right Software
Look for technical documentation software that is easy to use, lightweight, and widely supported. It should be ideal for version-controlled documentation and enable internal collaboration with internal comments.
Robust knowledge base tools enable advanced analytics to give you a bird’s eye view of the performance of your technical documentation – total searches, failed searches, articles created, total reads, popular and poorly rated articles, failed keywords, new articles created, and more.
| Related blog: Top 19 Online Documentation Software & Tools for 2024 |
Consistent Auditing & Updating
Regularly review your documentation. Correct inaccuracies, update screenshots and verify links. Clearly label versions (e.g., v1.0, v2.1). Archive outdated versions.
Encourage users to provide feedback. Use analytics to track popular pages and identify pain points.
Technical Documentation Examples
Technical documentation encompasses various formats and styles designed to cater to different informational requirements and user scenarios.
Below are some technical documentation examples that showcase the variety and effectiveness of technical documents across different sectors and uses.
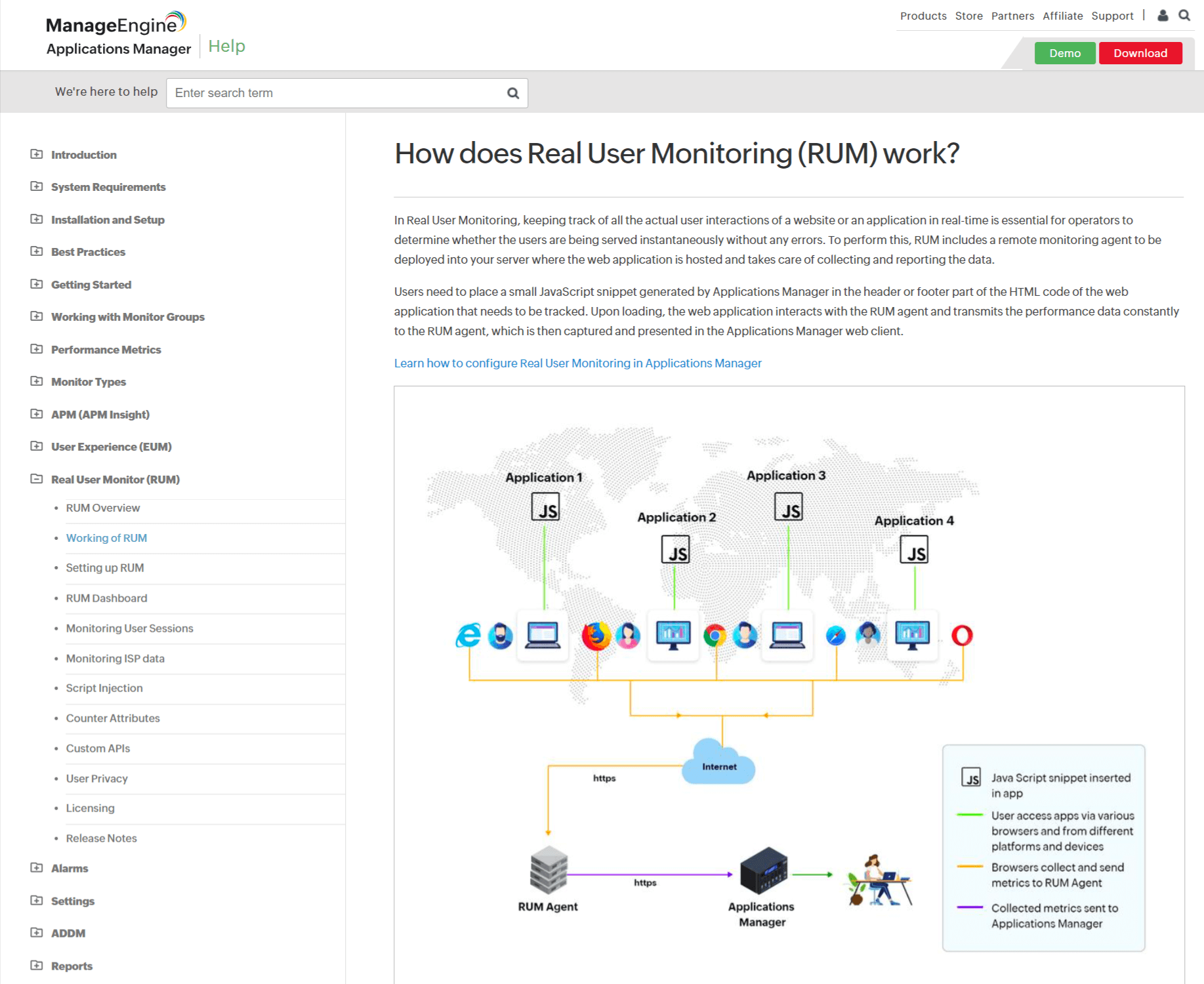
Manage Engine



Manage Engine’s documentation is a perfect balance between simple and professional language. It guides users effectively without overwhelming them.
The writing tone is informative yet avoid jargons. The documentation content is structured, with clear headings and concise explanations.
There are links within the page which connect users to relevant resources, and multimedia elements like the image representation enhance understanding.
RMS
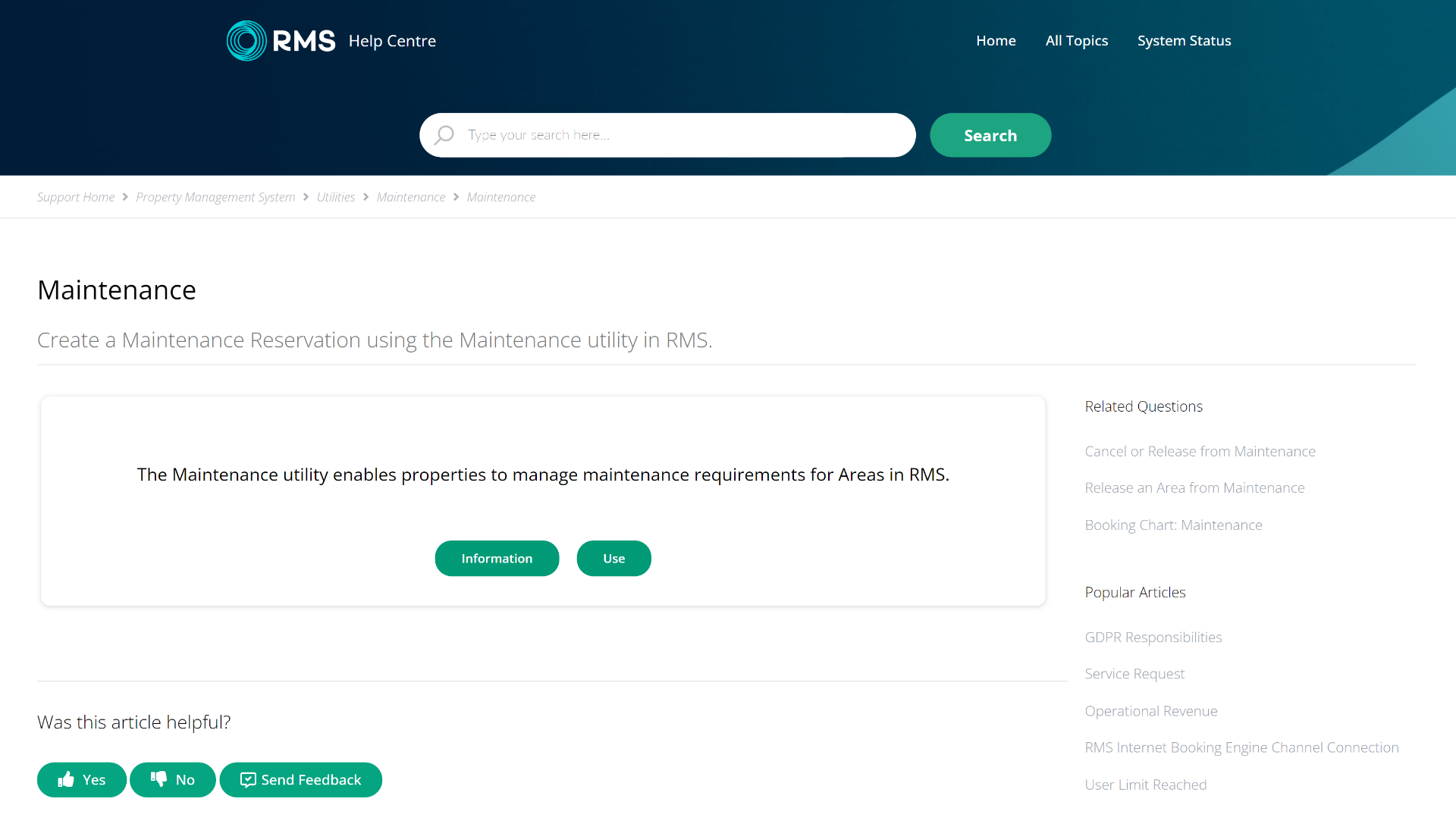

RMS’ technical documentation writing approach is simple, concise and task-oriented. It provides step-by-step instructions for users, focusing on practical solutions.
The page elements include clear and simple headings, useful links, and standard troubleshooting guides. The page also has a visual guide that enables better interactability and understandability.
CDS Convert
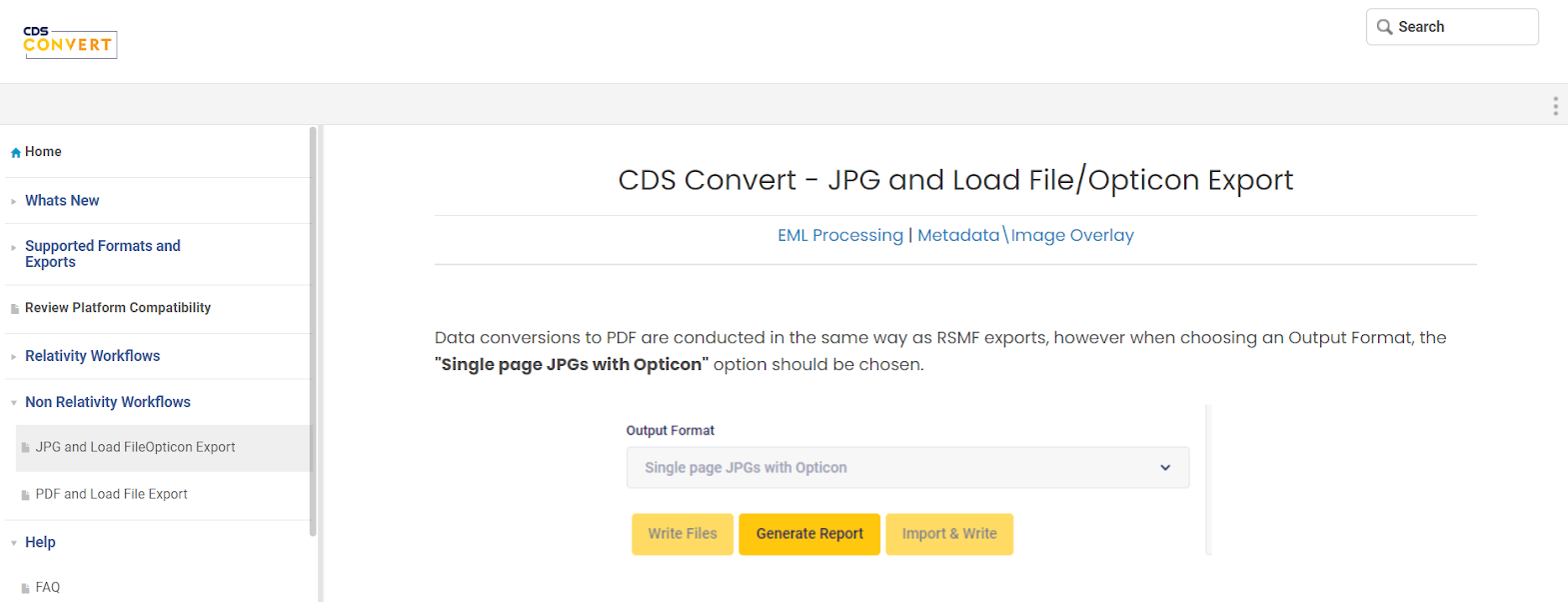

CDS Convert’s technical documentation is concise and task-oriented approach. Readers get structured content with clear headings, guiding them through the process.
Besides simple screenshots, the simple content ensures efficient problem-solving for users seeking guidance on PDF exports.
Improve Product Usabiity With Detailed Techncial Documentation
From guiding users through the intricacies of software to helping developers integrate APIs, the importance of technical documentation cannot be overstated.
Also, adhering to best practices in technical documentation enhances user satisfaction and engagement, facilitates smoother development processes, ensures compliance, and supports effective training and troubleshooting.
ProProfs Knowledge Base can help you simplify the process documentation with its user-friendly interface and intelligent, AI-powered WYSIWYG editor to create error-free technical content quickly.
You can easily tailor your documentation to match your brand’s look and feel, ensuring a consistent user experience across all touchpoints. Facilitate teamwork with features that allow multiple authors to contribute and edit documents, ensuring that your technical documentation benefits from collective expertise.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!